Taylor The Fiend
Telling the truth has become a revolutionary act, so let us salute those who disclose the necessary facts.
ALTERNATIVE NEWS
10 Jan 2026
James Fishback On DeSantis’s Attack On Free Speech, Randy Fine’s Bloodlust & America Last Globalism
Tucker Carlson: James Fishback is running for governor in Florida. Pretty soon, all winning Republican politicians will talk like this. Why Is James Fishback Running for Florida Governor? - How Florida's Economy Is Being Sabotaged - Randy Fine and Ron DeSantis's Anti-Free Speech Laws - Why Does Florida Give So Much Money to Israel? - How Randy Fine Tried to Intimidate Fishback Into Not Running - Is Byron Donalds Bought and Paid For? - The Identity Politics Taking Over the Right - Why Does Ben Shapiro Have So Much Disdain for White, Christian Men? - Fishback Responds to the Attacks Against Him - Why Fishback Changed His Views on Israel - Can Fishback Actually Win? - Florida Lt. Gov. Jay Collins Wants to Limit Free Speech
Trump Says US Will Begin Strikes On Cartels In Mexico
"We knocked out... the drugs coming in by water, and we are going to start now hitting land with regard with the cartels," the U.S. president said...
Authored by Joseph Lord and Kimberley Hayek: President Donald Trump announced in an interview aired Jan. 8 that the United States would begin launching strikes on cartels in Mexico.
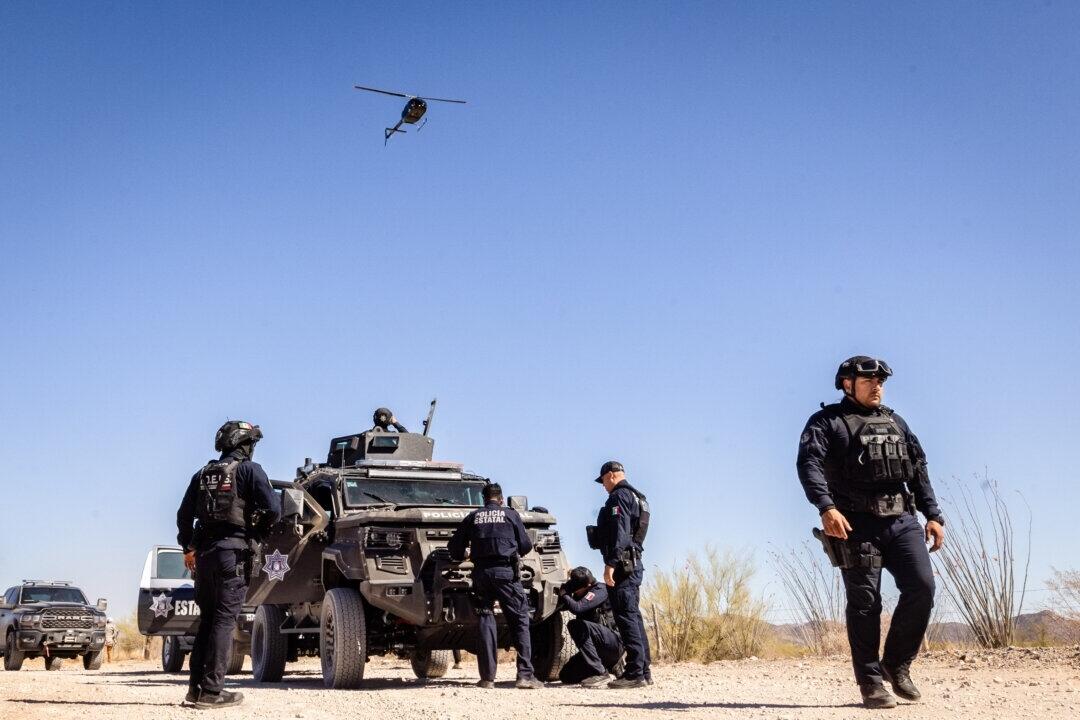

“The cartels are running Mexico. It’s very sad to watch and see what’s happened to that country.
“They’re killing 250,000, 300,000 in our country every single year.”
The announcement comes just five days after Trump ordered an operation to capture and remove Venezuelan leader Nicolás Maduro to the United States to face criminal charges, including narco-terrorism.
The Moment Orwellian Zionist Jew Bill 'Male Genital Mutilation MGM King' Gates Is Asked About His Plan For Humanity
'How philanthropy, Jew nobbled lame stream media deference and international health bodies converge to normalize permanent surveillance'
Russell Brand: When media outlets laugh off scrutiny of figures like Bill Gates while global institutions quietly draft blueprints for lifelong digital ID and vaccine compliance, this piece examines how public health rhetoric is used to shield power from interrogation. The focus is on how philanthropy, media deference, and international health bodies converge to normalize permanent surveillance, linking identity, health status, and compliance from birth onward. The question isn’t whether vaccines exist, but who gets to question systems that turn care into control before refusal becomes impossible. [UNPACKED]
Three Takeaways From Trump's Seizure Of A Russian-Flagged Tanker In The Atlantic
'Enforcing the maritime component of “Fortress America” is so important for Trump 2.0 that it’s willing to rubbish the “rules-based order” over it and even risk an accidental war with Russia.'
Authored by Andrew Korybko: The overarching trend is that the US is militarily reasserting its historical “sphere of influence” over the Americas, and enforcing the maritime component of “Fortress America” is so important for Trump 2.0 that it’s willing to rubbish the “rules-based order” over it and even risk an accidental war with Russia.
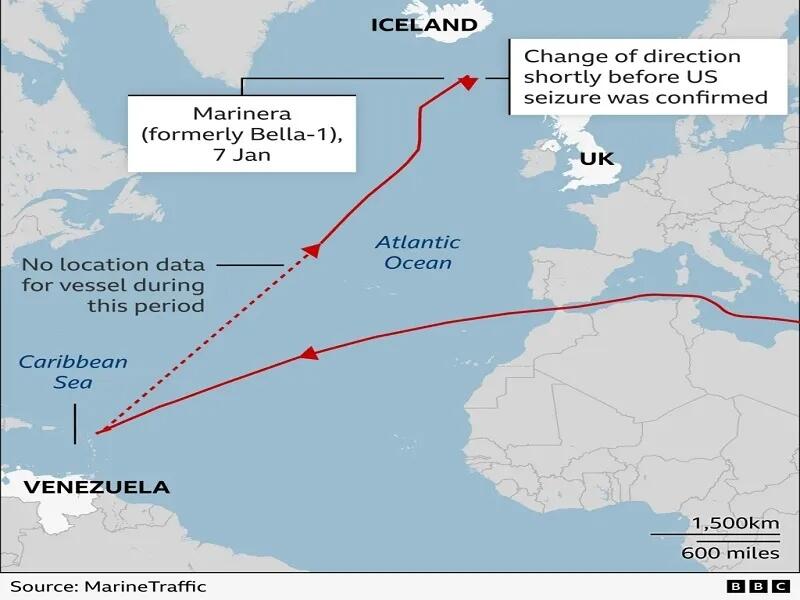
The Russian-flagged Marinera tanker was just seized by the US in the Atlantic. It was earlier named the Bella 1 and is under US sanctions due to connections to Hezbollah. It sailed under the Guyanese flag from Iran to Venezuela and attempted to break the US’ blockade. It failed, turned around, changed its name to the Marinera, and received a temporary permit to sail under the Russian flag before being seized. Russian then demanded that its citizens on board be treated humanely and returned home.
Amyloid Clots Found in EVERY SINGLE PERSON After 2022: Brand New Study
EONutrition: In this video I discuss the results of a brand new study which found amyloid microclots in every single participant. I explain what this means, why it's important, and what you might be able to do about it.
How A Techno-Optimist Became A Grave Skeptic
A system that assumes benevolent, self-correcting governance is no safer than one that assumes benevolent, aligned superintelligence.
Authored by Roger Bate: Before Covid, I would have described myself as a technological optimist. New technologies almost always arrive amid exaggerated fears. Railways were supposed to cause mental breakdowns, bicycles were thought to make women infertile or insane, and early electricity was blamed for everything from moral decay to physical collapse. Over time, these anxieties faded, societies adapted, and living standards rose. The pattern was familiar enough that artificial intelligence seemed likely to follow it: disruptive, sometimes misused, but ultimately manageable.
Across much of the world, governments and expert bodies responded to uncertainty with unprecedented social and biomedical interventions, justified by worst-case models and enforced with remarkable certainty. Competing hypotheses were marginalized rather than debated. Emergency measures hardened into long-term policy. When evidence shifted, admissions of error were rare, and accountability rarer still. The experience exposed a deeper problem than any single policy mistake: modern institutions appear poorly equipped to manage uncertainty without overreach.
The Camel Always Tries To Put Its Nose Under The Tent + "Britain Is Such An Emaciated Husk Of A Country"
"We [USA] are a rogue nation today ruled by a CALIGULA like dictator, a narcissist that mutes any notion of constitutional, or international law. ...The US has chosen to engage in acts of PIRACY, illegal acts."
George Galloway: The remedy is to thwack it. So how will Russia respond to the seizure of two of its tankers? Scott Ritter on America's illegal act of piracy in the North Atlantic and Caribbean and what now?
The Price Of Trump's "Greenland New Deal": $100,000 Per Person
US officials have discussed lump sum payments of $10,000 to $100,000 per Greenlander in order to convince them to become part of the United States
By Bas van Geffen: President Trump has called for a 50% increase of the US defense budget, to $1.5 trillion by next year. This should suffice to build a “Dream Military.” The president argues this is required to keep the US safe and secure, but will it keep his own political position safe? Trump’s new military focus is creating more friction in Congress, as well as between the US and its allies.
Trump argued that tariff revenues can “easily” pay for a bigger defense budget, but the CBO has estimated that tariff revenues will only generate about half of the president’s planned increase in military expenditures. And that assumes these revenues will keep flowing. Trump could face a setback on that front as early as today (see below).Another Coup Attempt In Burkina Faso: TRAORÉ HIT?!
Zack Mwekassa: Burkina Faso is once again at the center of political chaos. Reports are emerging of another coup attempt targeting President Ibrahim Traoré, sending shockwaves across Africa and the international community.


